Farewell RMF, Hello CSRMC!
Today the U.S. Department of War (DoW) surprised us all.
Inside this Edition
Here’s what we got for you today:
Next-Gen Cyber Defense: DoW Unveils New Cybersecurity Risk Management Construct
Links to some of our most popular articles.
GRC Spotlight
Next-Gen Cyber Defense: DoW Unveils New Cybersecurity Risk Management Construct
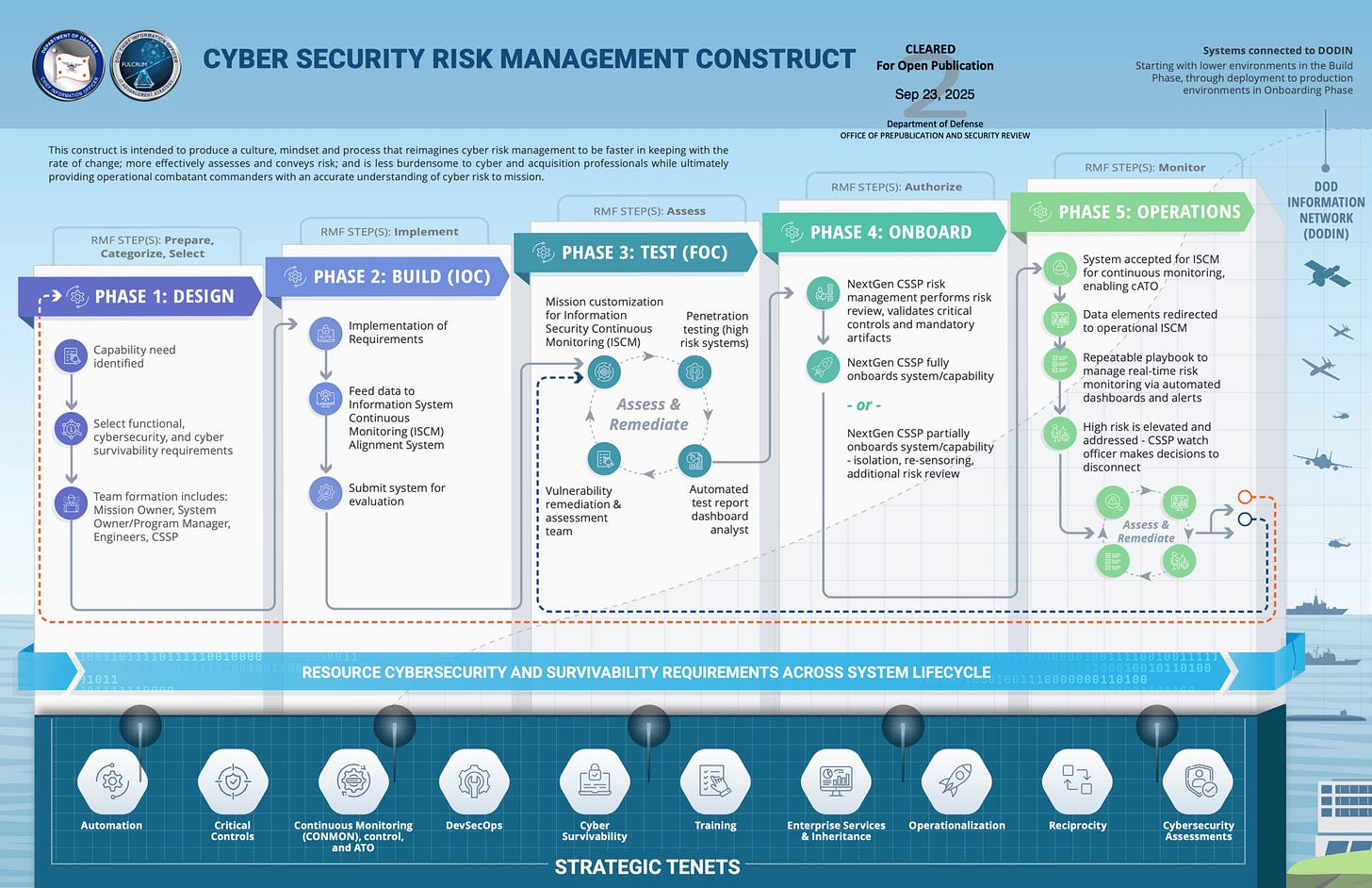
The Department of War (DoW) has announced a significant evolution in its approach to cybersecurity with the introduction of the new Cybersecurity Risk Management Construct (CSRMC). This move marks a departure from the long-standing NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF), signaling a shift towards a more dynamic and automated approach to cyber defense.
You can read the full announcement here.
The DoW states the RMF has become "overly reliant on static checklists and manual processes that failed to account for operational needs and cyber survivability requirements." The CSRMC, in contrast, aims to enable "cyber defense at the speed of relevance required for modern warfare" by focusing on automation, critical controls, and continuous monitoring.
The New 5-Phase Lifecycle
At the heart of the CSRMC is a five-phase lifecycle that aligns with system development and operations:
Design Phase: Security is embedded at the outset, ensuring resilience is built into the system architecture.
Build Phase: Secure designs are implemented as systems achieve Initial Operating Capability (IOC).
Test Phase: Comprehensive validation and stress testing are performed prior to Full Operating Capability (FOC).
Onboard Phase: Automated continuous monitoring is activated at deployment to sustain system visibility.
Operations Phase: Real-time dashboards and alerting mechanisms provide immediate threat detection and rapid response.
From 7 Steps to 5 Phases: A Paradigm Shift
The CSRMC's five phases represent a streamlined and more integrated approach compared to the seven steps of the NIST RMF:
RMF Steps
CSRMC Phase
1. Prepare
Phase 1: Design
2. Categorize
Phase 1: Design
3. Select
Phase 1: Design
4. Implement
Phase 2: Build
5. Assess
Phase 3: Test
6. Authorize
Phase 4: Onboard
7. Monitor
Phase 5: Operations
Key Takeaways
The introduction of the CSRMC signifies a major shift in the DoW's cybersecurity strategy, with a clear emphasis on:
Automation: To increase the speed and efficiency of risk management.
Continuous Monitoring: To achieve real-time situational awareness and a constant state of authorization.
Integration: Embedding security into the development lifecycle from the very beginning (DevSecOps).
Cyber Survivability: Enabling operations to continue even in contested cyber environments.
This new construct is not just a replacement for the RMF; it's a fundamental change in mindset, moving from a compliance-based approach to a risk-based, operational, and data-centric model. As the DoW rolls out the CSRMC, contractors and stakeholders can expect a greater emphasis on automated security solutions, real-time data, and a more agile and responsive approach to cybersecurity.
Test your Knowledge
Today’s question is from the CISM curriculum:
Which of the following is MOST important for ensuring data integrity during a disaster recovery process?
A) Encryption
B) Data validation checks
C) Backup frequency
D) Physical security measures
👉 Think you know the answer? Scroll down for the solution!
Answer: The correct answer is B.
A) Encryption is important for security but not directly related to data integrity during recovery.
B) Data validation checks ensure that the data being restored is accurate.
C) Backup frequency is important but secondary to data validation.
D) Physical security measures are important but not directly related to data integrity during recovery.